Blockchain Technology Explained: How It Works & Why It Matters
Introduction
Blockchain technology is revolutionizing various industries, from finance and healthcare to supply chain and security. Originally developed as the underlying technology for Bitcoin, blockchain has since evolved into a powerful tool for decentralization, transparency, and security. In this guide, we will break down how blockchain works and why it is crucial in today’s digital world.
What is Blockchain?
Blockchain is a distributed ledger technology (DLT) that records transactions across multiple computers securely and transparently. Each block in the chain contains transaction data, a timestamp, and a cryptographic hash linking it to the previous block, ensuring data integrity.
Key Features of Blockchain:
- Decentralization: No single entity controls the network.
- Transparency: Transactions are publicly recorded and verifiable.
- Security: Cryptographic encryption prevents tampering.
- Immutability: Once recorded, transactions cannot be altered.
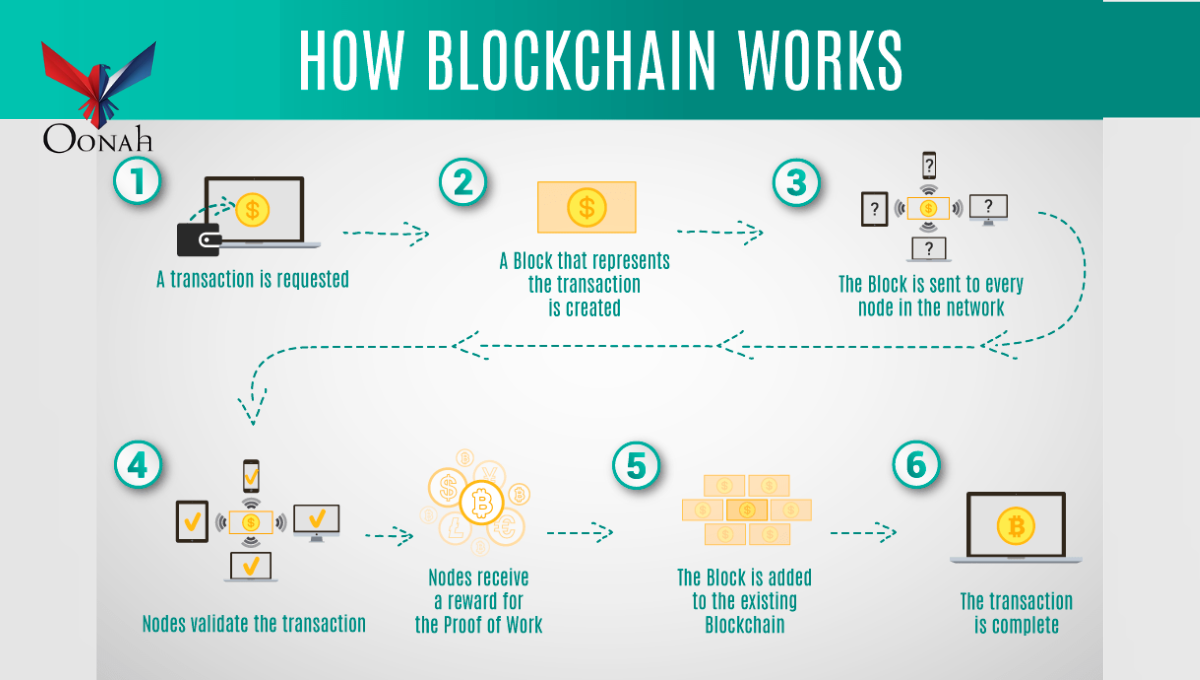
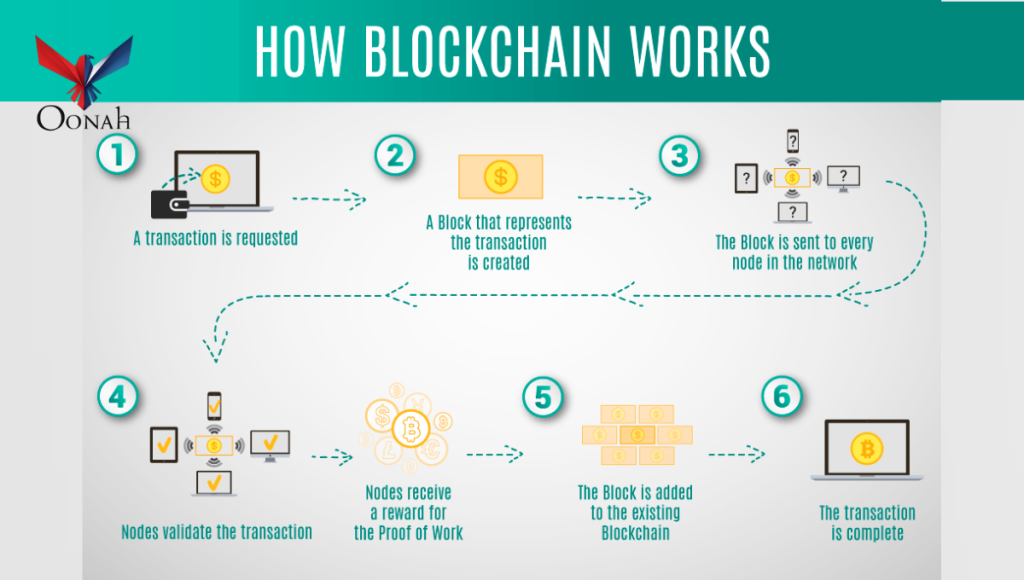
How Blockchain Works
Blockchain operates on a peer-to-peer network where nodes (computers) validate and record transactions. Here’s a simplified breakdown:
- Transaction Initiation: A user requests a transaction (e.g., sending cryptocurrency).
- Verification: The network nodes validate the transaction using consensus mechanisms.
- Block Formation: Once verified, the transaction is grouped with others into a block.
- Hashing & Linking: The new block is cryptographically linked to the previous block.
- Finalization: The transaction is recorded permanently on the blockchain.
Types of Blockchain Networks
1. Public Blockchains
- Open to anyone (e.g., Bitcoin, Ethereum).
- Decentralized with high security but lower scalability.
2. Private Blockchains
- Restricted access, controlled by a single organization.
- Faster transaction speeds but less decentralized.
3. Consortium Blockchains
- Shared control among multiple organizations.
- Used for business collaborations and supply chain management.
4. Hybrid Blockchains
- Combines public and private blockchain elements.
- Offers a balance between security and efficiency.
Applications of Blockchain Technology
1. Cryptocurrency & Payments
- Enables secure, transparent, and borderless transactions.
- Popular examples: Bitcoin (BTC), Ethereum (ETH), and Binance Coin (BNB).
2. Smart Contracts
- Self-executing agreements with predefined rules.
- Used in finance, real estate, and legal sectors.
3. Supply Chain Management
- Tracks product movement and authenticity.
- Improves efficiency and reduces fraud.
4. Healthcare & Data Security
- Secure storage of patient records.
- Ensures data integrity and privacy.
5. Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
- Removes intermediaries in financial transactions.
- Enables lending, borrowing, and yield farming.
Benefits of Blockchain Technology
- Enhanced Security: Cryptographic encryption prevents hacking.
- Transparency: Every transaction is publicly verifiable.
- Reduced Costs: Eliminates intermediaries in financial transactions.
- Faster Transactions: Cross-border payments settle within minutes.
- Data Integrity: Tamper-proof records ensure accuracy.
Challenges & Limitations of Blockchain
- Scalability Issues: High transaction fees and slow processing times.
- Energy Consumption: Proof-of-Work (PoW) blockchains require significant electricity.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: Governments are still developing policies for blockchain use.
- Adoption Barriers: Businesses require technical expertise to integrate blockchain solutions.
The Future of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain is expected to revolutionize industries through:
- Integration with Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI-powered blockchain applications.
- Advancements in Layer 2 Solutions: Faster and cheaper transactions.
- Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs): Government-backed digital currencies.
- Enterprise Blockchain Adoption: More businesses implementing blockchain for security and transparency.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology is shaping the future of digital transactions, security, and decentralization. Whether in cryptocurrency, finance, supply chains, or healthcare, blockchain’s impact is undeniable. Businesses and individuals should stay informed and explore blockchain applications to leverage its benefits effectively.
🚀 Explore More Cryptocurrency Insights:
- How to Earn Passive Income with Crypto Staking – Maximize your earnings through staking.
- Best Low-Cost Cryptocurrencies to Invest in 2025 – Discover affordable crypto investment opportunities.
- Top DeFi Yield Farming Strategies for Passive Income – Learn how to generate profits in the DeFi space.
- Best AI-Powered Crypto Trading Bots – Automate your crypto trading strategies.
- AI-Powered SEO & Marketing Automation – Leverage AI for better marketing strategies.
👉 Stay updated with the latest crypto and blockchain trends at oonah.xyz!